這次的目標是寫一個能利用 API Hook 來注入自訂功能的工具,我選用了 Debug API 這個方法以除錯法的方式來進行注入,那先看看成果如何 :
本程式在 x64 Windows 10 確認可以執行。
https://github.com/Dinlon5566/IT_Reverse_Engineering/tree/main/Dx25
WriteFile() 被調用,把他傳入的文字修改成全部大寫。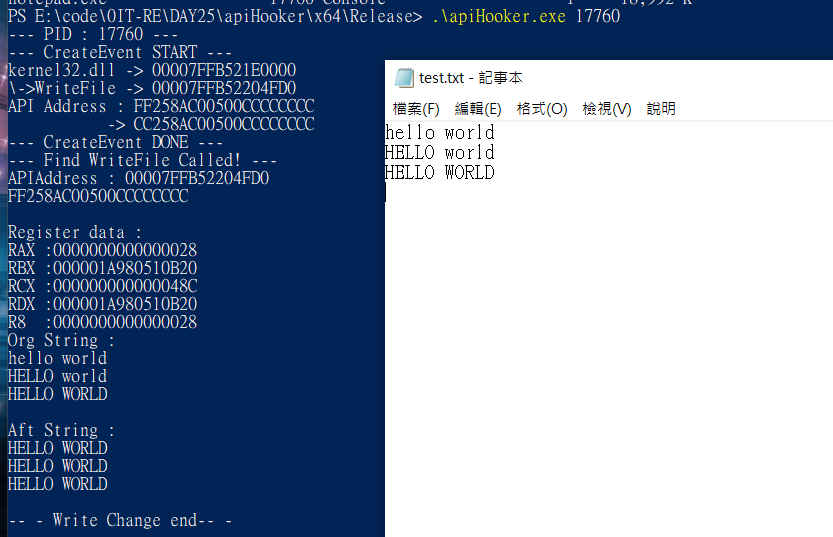
如果存檔時發現記事本無回應,請立即使用工作管理員把記事本關閉。否則會一直寫入錯誤的記憶體區間導致卡死。這是因為新增檔案的時候並不是使用
WriteFile(),插入的 Hook 未取出所導致的記憶體存取錯誤。
那先來看看,這個工具實際上要如何製作呢 ? 首先先看簡單的流程 :
StayDebugEvent() 等待事件發生doCreateEvent()。
WriteFile() 位置0xCC。當程序碰到 0xCC 時會觸發 INT3 例外,由此把程序交到 Deubger (注入器) 手上。doExceptionEvent()。
StayDebugEvent()
API Hook 的很多東西,等等慢慢講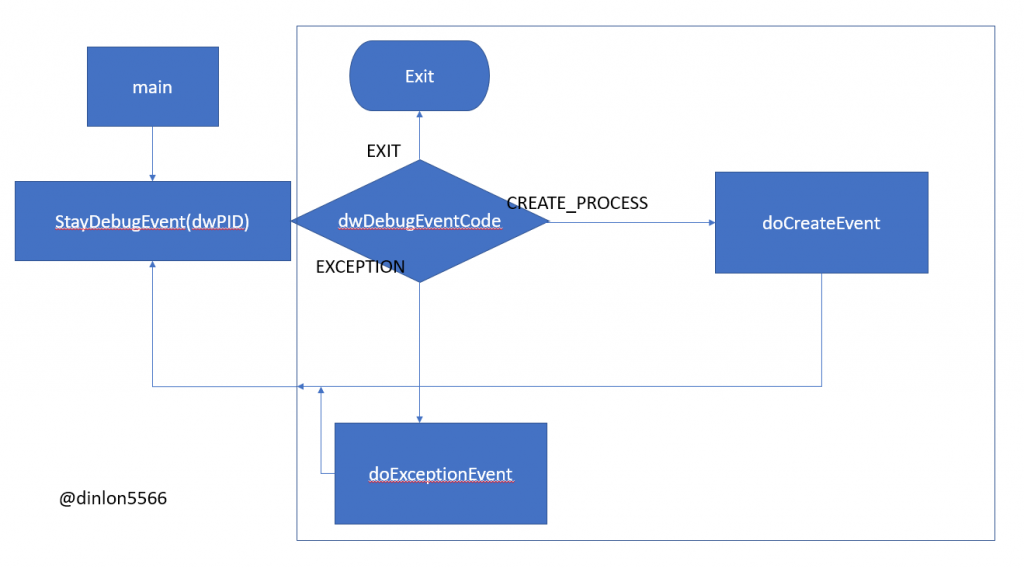
那我們開始吧,程式碼裡的註解說明了指令的功能與目標 :
首先,main() 的部分像這樣。
先把參數轉為數字做為 PID,利用 DebugActiveProcess() 來檢查目標程序是否存在。
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {
if (argc != 2) {
printf("USEAGE : apiHooker.exe <PID> \n");
// 這一行方便我取用 notepad.exe 的 PID
system("tasklist | findstr notepad");
return 1;
}
DWORD dwPID = atol(argv[1]);
if (!dwPID) {
printf("PID error!");
return 0;
}
printf("--- PID : %d ---\n", dwPID);
// 檢查是否程序是否存在
if (!DebugActiveProcess(dwPID)) {
printf("Debug Fail\n");
printf("Error code : %d", GetLastError());
return 1;
}
StayDebugEvent();
return 0;
}
等待事件的地方,當有事件時 WaitForDebugEvent 就會把事件發到 debugEvent,透過比對 EventCode 來判斷事件類型。之後並把 debugEvent 作為媒介發給 doCreateEvent() 與 doExceptionEvent() 方便之後直接利用。
當一圈跑完之後需要 Continue 讓事件後的指令繼續跑下去。
BOOL StayDebugEvent() {
DEBUG_EVENT debugEvent;
DWORD dwStat;
// 等待事件發生
while (WaitForDebugEvent(&debugEvent, INFINITE)) {
if (debugEvent.dwDebugEventCode == CREATE_PROCESS_DEBUG_EVENT) {
doCreateEvent(&debugEvent);
}
else if (debugEvent.dwDebugEventCode == EXCEPTION_DEBUG_EVENT)
{
doExceptionEvent(&debugEvent);
}
else if (debugEvent.dwDebugEventCode == EXIT_PROCESS_DEBUG_EVENT) {
printf("Process %d is down!\n", debugEvent.dwProcessId);
break;
}
// 繼續跑下去
ContinueDebugEvent(debugEvent.dwProcessId, debugEvent.dwThreadId, DBG_CONTINUE);
}
return 1;
}
首先這邊是宣告的變數
// 用來存 WriteFile 的位置
LPVOID pfWriteFile = NULL;
// 放置 CREATE_PROCESS 時的資料(來自於debugEvent->u.CreateProcessInfo)
CREATE_PROCESS_DEBUG_INFO debugInfo;
// 用於放置替換資料與備份資料 (第一個 BYTE),0xCC藉此觸發INT3斷點異常
BYTE chINT3 = 0xCC, chOrgByte = 0;
看到 doCreateEvent :
主要用於把函式庫的位置記下來,並把 Hook 接上去。使 0xCC INT3 例外發生時就會觸發事件。
BOOL doCreateEvent(LPDEBUG_EVENT debugEvent) {
printf("--- CreateEvent START ---\n");
//取得函式庫與得到 WriteFile API 的位置
HMODULE module = GetModuleHandleA("kernel32.dll");
pfWriteFile = GetProcAddress(module, "WriteFile");
//輸出
printf("kernel32.dll -> %p\n", module);
printf("\\->WriteFile -> %p\n", pfWriteFile);
// 將 debugEvent 的 CreateProcessInfo 寫到 debugInfo,u.CreateProcessInfo 的結構為 CREATE_PROCESS_DEBUG_INFO。
// https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/win32/api/minwinbase/ns-minwinbase-debug_event
memcpy(&debugInfo, &debugEvent->u.CreateProcessInfo, sizeof(CREATE_PROCESS_DEBUG_INFO));
// 讀入目標程序的 pfWriteFile 位置。
BYTE arr[10];
ReadProcessMemory(debugInfo.hProcess, pfWriteFile, arr , sizeof(BYTE)*10, NULL);
// 用來還原 API 位置
chOrgByte = arr[0];
printf("API Address : ");
for (BYTE i : arr) {
printf("%02X", i);
}
// 將第一個 BYTE 改成 0xCC 接上 Hook
WriteProcessMemory(debugInfo.hProcess, pfWriteFile, &chINT3, sizeof(BYTE), NULL);
// 讀入更改後的WriteFile並顯示 (其實不需要這個步驟)
ReadProcessMemory(debugInfo.hProcess, pfWriteFile, arr, sizeof(arr), NULL);
printf("\n -> ");
for (BYTE i : arr) {
printf("%02X", i);
}
printf("\n--- CreateEvent DONE ---\n");
return 1;
}
BOOL doExceptionEvent(LPDEBUG_EVENT debugEvent) {
CONTEXT context;
PBYTE pBuf = NULL;
ULONG_PTR ulpWriteLen, ulpBufAddress;
PEXCEPTION_RECORD64 debugRecord = (PEXCEPTION_RECORD64)&debugEvent->u.Exception.ExceptionRecord;
BYTE arr[10];
// 確認 Exception 的位置為原本的 WriteFile 位置,正是設立INT3中斷的位置。
if (debugRecord->ExceptionCode == EXCEPTION_BREAKPOINT &&
debugRecord->ExceptionAddress==(DWORD64)pfWriteFile
) {
printf("--- Find WriteFile Called! ---\n");
printf("APIAddress : %p\n",(DWORD64)pfWriteFile);
// 把之前改過的 API 位置改回去( 取走 Hook )
WriteProcessMemory(debugInfo.hProcess, pfWriteFile, &chOrgByte, sizeof(BYTE), NULL);
// 輸出 API 位置
ReadProcessMemory(debugInfo.hProcess, pfWriteFile, arr, sizeof(arr), NULL);
for (BYTE i : arr) {
printf("%02X", i);
}
printf("\n");
在取得我們輸入的資料的時候,必須得到暫存器中的值用於獲得 notepad.exe 傳遞給 WriteFile() 的參數,可以透過以下來查看暫存器的資料
// 取得 Register
context.ContextFlags = CONTEXT_FULL;
GetThreadContext(debugInfo.hThread,&context);
// 輸出 Register,方便查看
printf("\nRegister data :\n");
printf("RAX :%p\n", context.Rax);
printf("RBX :%p\n", context.Rbx);
printf("RCX :%p\n", context.Rcx);
printf("RDX :%p\n", context.Rdx);
printf("R8 :%p\n", context.R8);
這邊直接指明 RDX 是存放字串的地方,而 R8 傳遞了資料的長度。
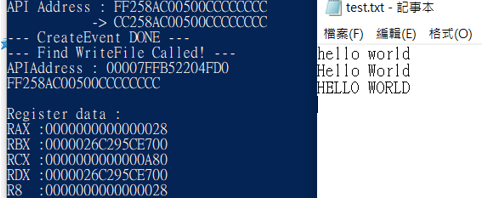
可以透過查看檔案來確認 28 為文件大小 :

接下去
// 將傳遞值由寄存器撈上來
ulpBufAddress = context.Rdx;
ulpWriteLen = context.R8;
// 宣告緩衝區空間與清空
pBuf = (PBYTE)malloc(ulpWriteLen+1);
memset(pBuf,0,ulpWriteLen+1);
// 讀取文字位置的內容到緩衝區
ReadProcessMemory(debugInfo.hProcess,(LPVOID)ulpBufAddress,pBuf,ulpWriteLen,NULL);
printf("Org String :\n%s\n",pBuf);
// 把字都變成大寫
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < (unsigned int)ulpWriteLen; i++) {
if ('a' <= pBuf[i] && pBuf[i] <= 'z') {
pBuf[i] -= 0x20;
}
}
printf("Aft String :\n%s\n", pBuf);
// 將緩衝區內容存到原本放字串的位置
WriteProcessMemory(debugInfo.hProcess,(LPVOID)ulpBufAddress,pBuf,ulpWriteLen,NULL);
// 緩衝區沒用了,釋放掉
free(pBuf);
// 把執行位置調到 WriteFile 的位置
context.Rip = (DWORD64)pfWriteFile;
// 然後把 Context 的資料設置給 Thread
SetThreadContext(debugInfo.hThread,&context);
// 原程序可以繼續行動了
ContinueDebugEvent(debugEvent->dwProcessId,debugEvent->dwThreadId,DBG_CONTINUE);
// 把 WriteFile 的第一 BYTE 改回 0xCC ( 把 Hook 放回去 )
WriteProcessMemory(debugInfo.hProcess, pfWriteFile, &chINT3, sizeof(BYTE),NULL);
printf("-- - Write Change end-- - \n");
}
return 1;
}
這篇主要是在程式中學習如何利用除錯法來進行 API HOOK,在使用 DEBUG API 寫了這份程式後就會發現其實看起來有很多東西,不過實際上流程是很明確的。但是在編輯的時候記憶體控制要很精確,不然就會發生這種東西 :
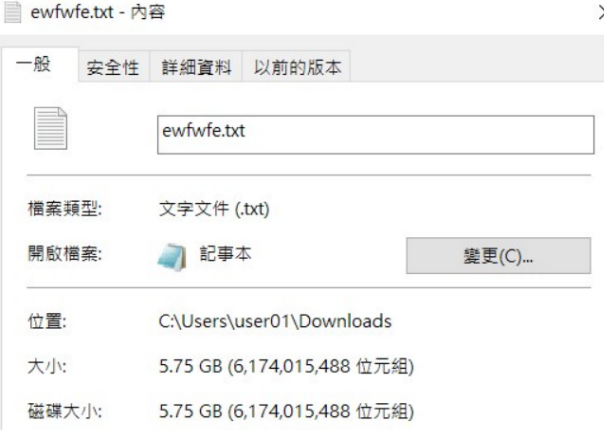
對。快 6 GB 的文件檔,差點把電腦搞壞 : /
寫這種東西時討厭的是因為系統架構不同 ( 像是 XP / Win7 / Win10 ),導致以前的代碼無法在新架構上使用,都要到各個地方查資料很花時間。
資料來源 :
https://www.codeproject.com/Articles/43682/Writing-a-basic-Windows-debugger
https://www.cnblogs.com/UnGeek/p/3515995.html
https://www.cnblogs.com/whitehawk/p/11166557.html
https://www.apriorit.com/dev-blog/727-win-guide-to-hooking-windows-apis-with-python
